GitHub Actions Workshop
Master GitHub Actions with hands-on labs and exercises. Learn how to automate workflows, run tests, deploy applications, and more using GitHub's powerful automation platform. This repository has everything you need to get started with continuous integration and continuous deployment.
Project maintained by prasadhonrao Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Lab: Environments, Variables, and Secrets
Introduction
In this lab, you will learn how to set up different environments in GitHub and how to use environment variables and secrets. You will also learn how to reference those variables and secrets in your workflows.
Estimated Duration: 30-40 minutes
Instructions
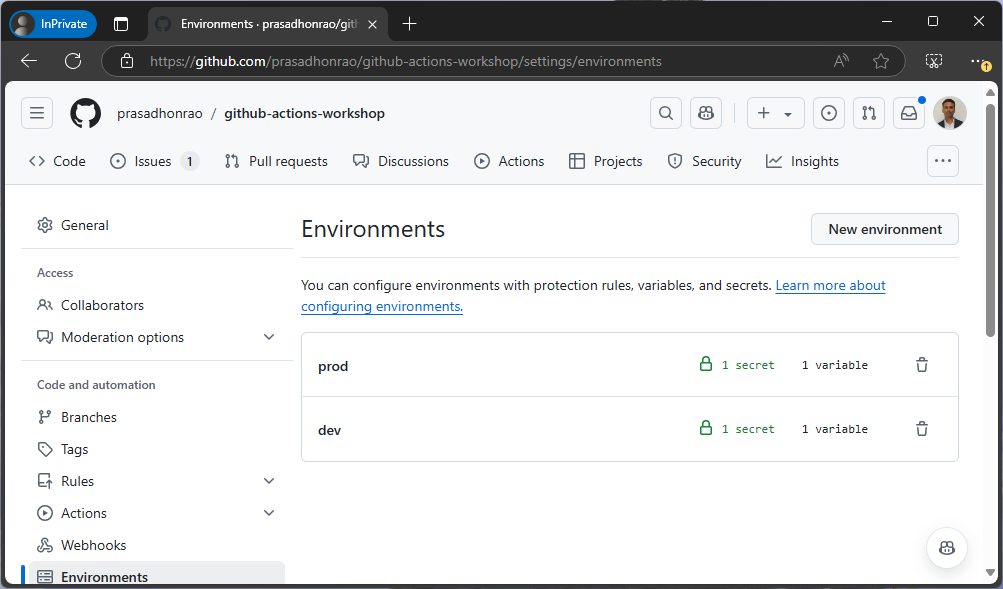
Step 1: Create Environments
-
Go to your repository on GitHub.
-
Click on the
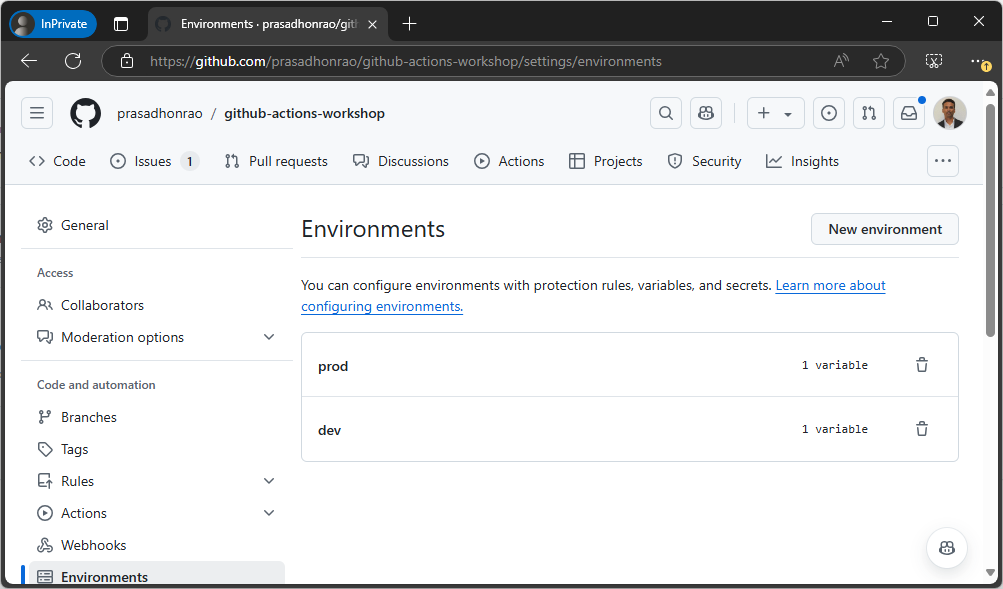
Settingstab and navigate to theEnvironmentssection on the left sidebar.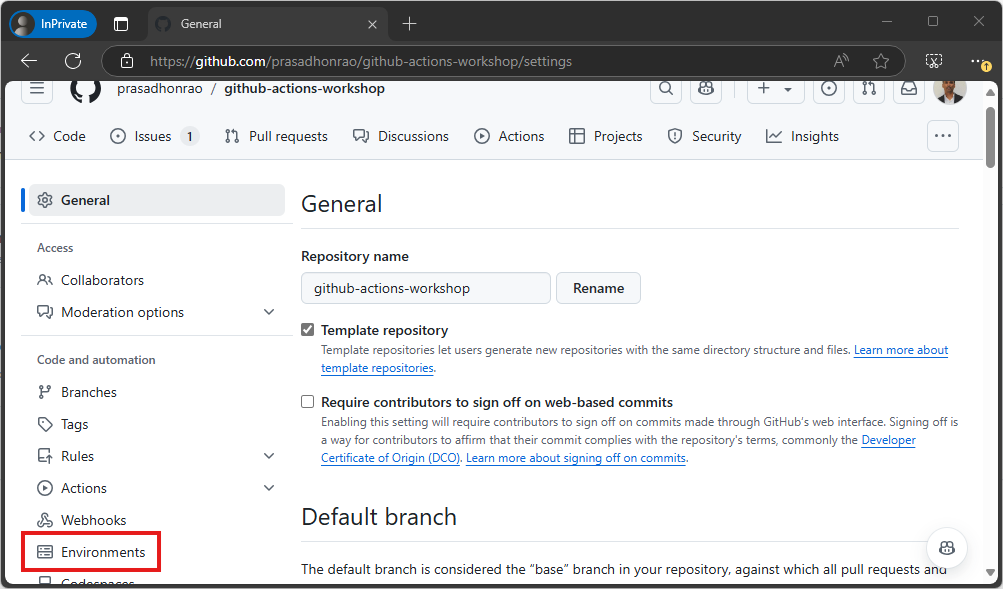
-
Click on
Environments. This will show you the list of environments, which should be empty if you have not created any environments earlier.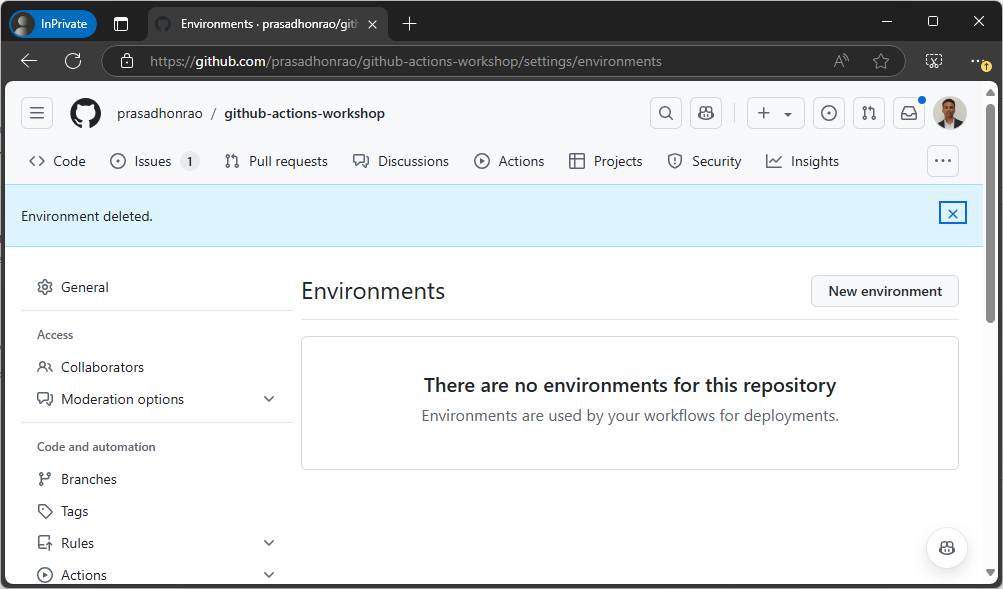
-
Click on
New environmentbutton.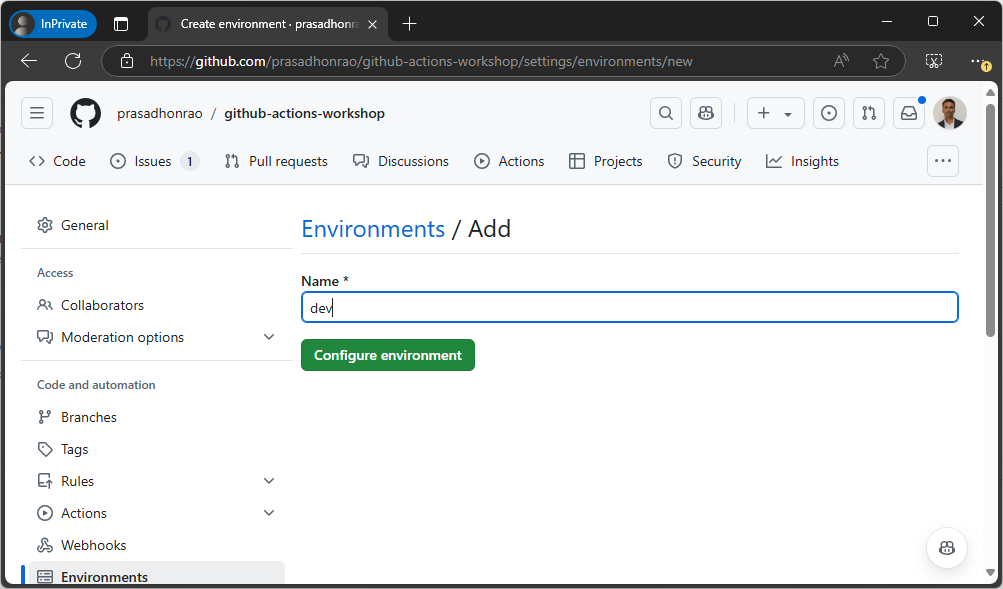
-
Enter the environment name as
devand click theCreate environmentbutton. -
Repeat steps 4 and 5 to create another environment named
prod. You should now see both thedevandprodenvironments in the list.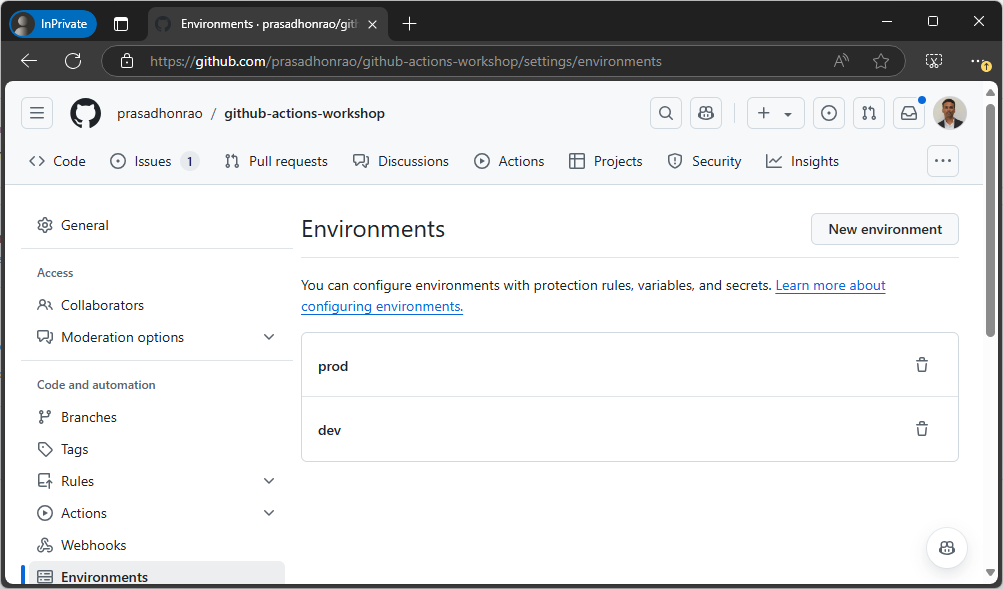
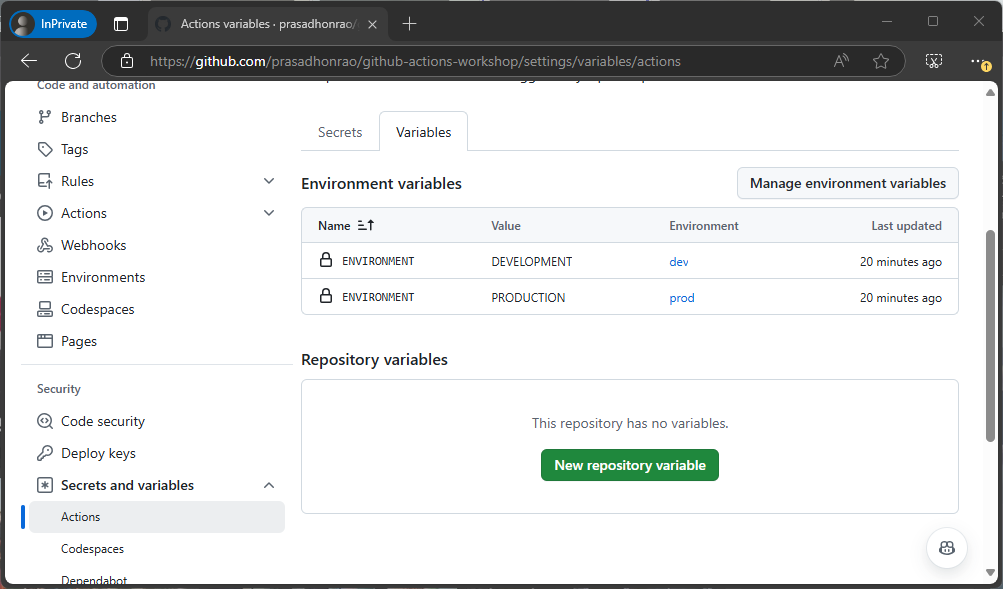
Step 2: Add Environment Variables
-
Select the
devenvironment and scroll down to the Environment variables section. Click on the Add environment variable button.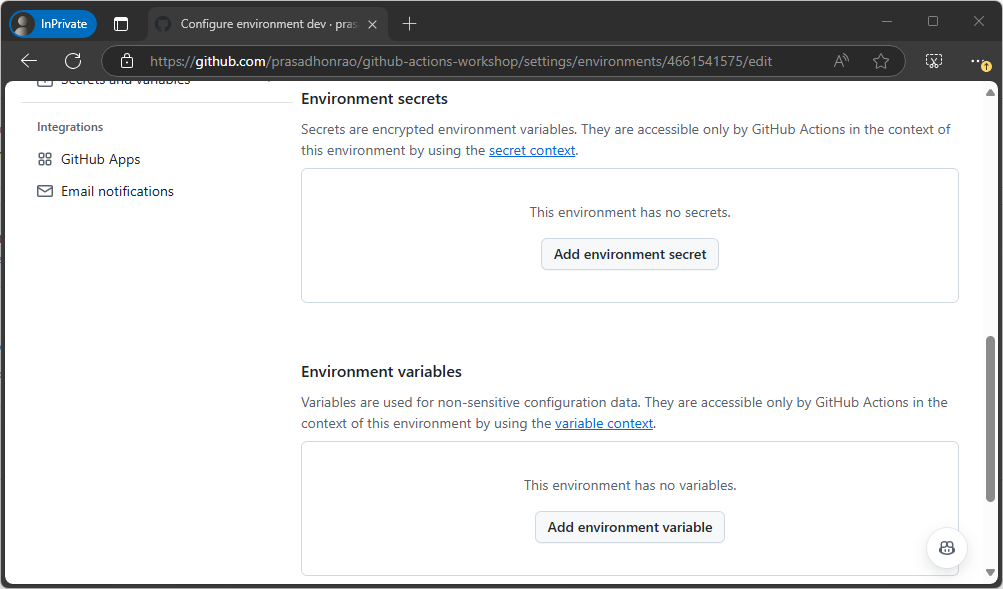
-
Enter the name as
ENVIRONMENTand the value asDEVELOPMENT. Click the Add variable button.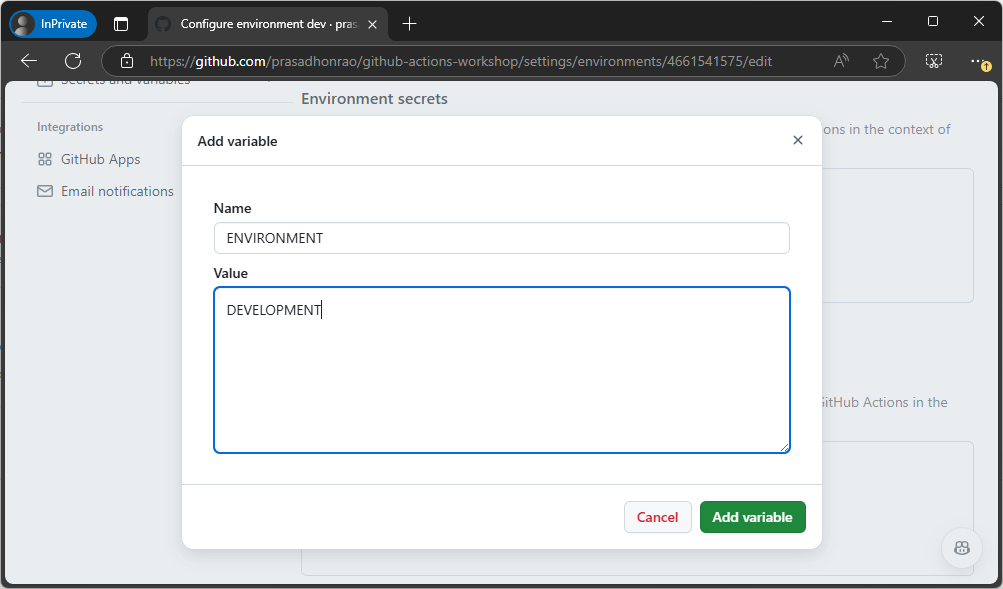
-
Repeat steps 1 to 3 for the
prodenvironment, but with the value set toPRODUCTION.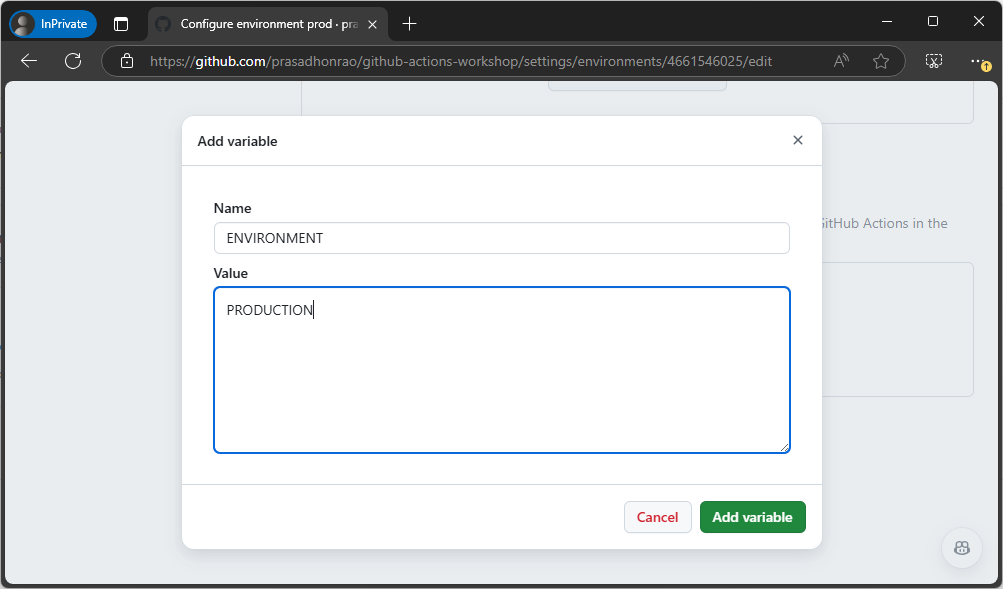
-
Both environment variables should now be added to their respective environments.
Step 3: Add Environment Secrets
-
Select the
devenvironment again and scroll down to the Environment secrets section. Click the Add environment secret button.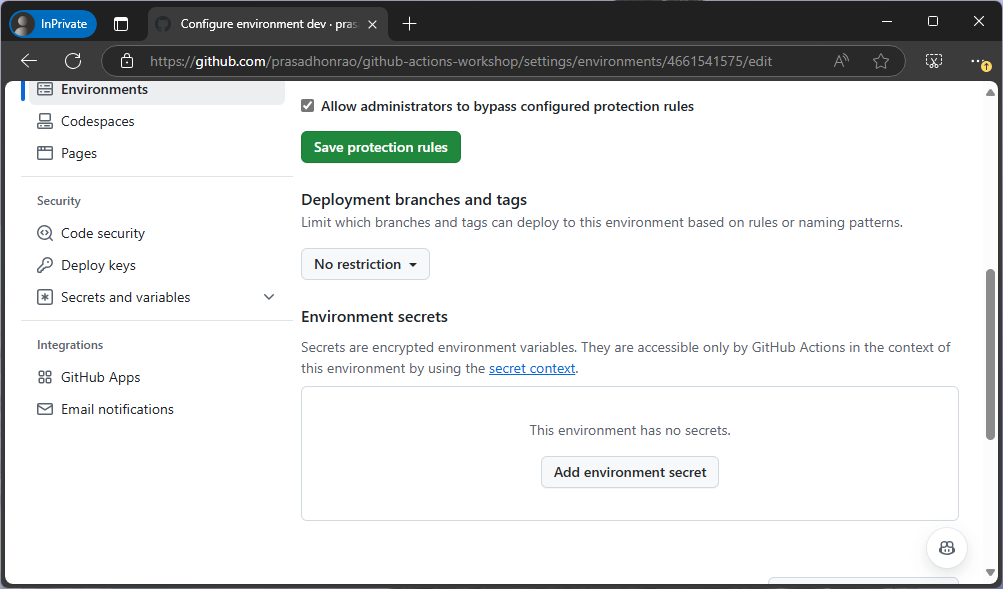
-
Enter the name as
SECRETand the value asSUPER SECRET DEV PASSWORD. Click the Add secret button.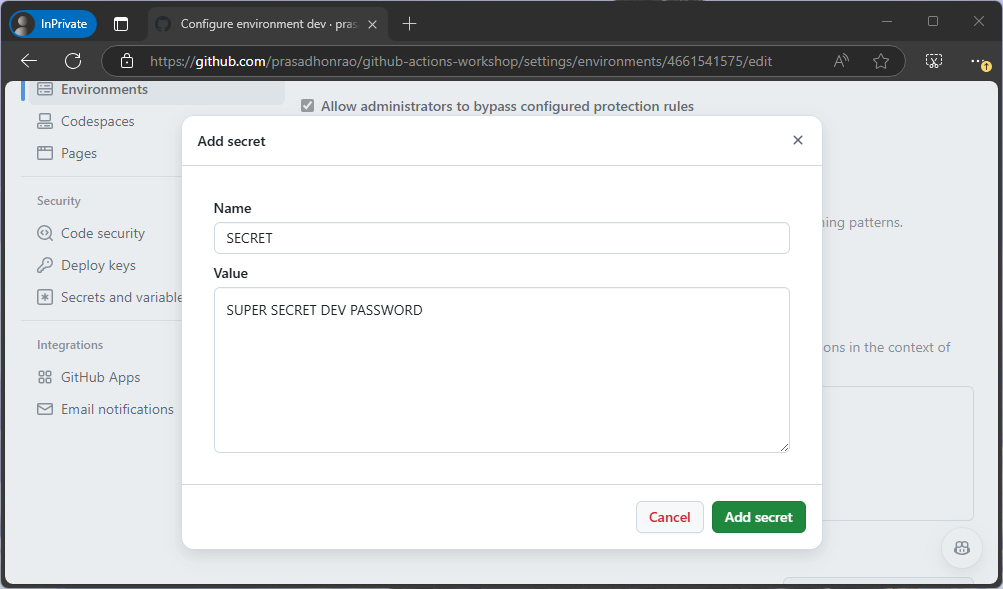
-
Repeat steps 1 to 3 for the
prodenvironment, but with the value set toSUPER SECRET PROD PASSWORD.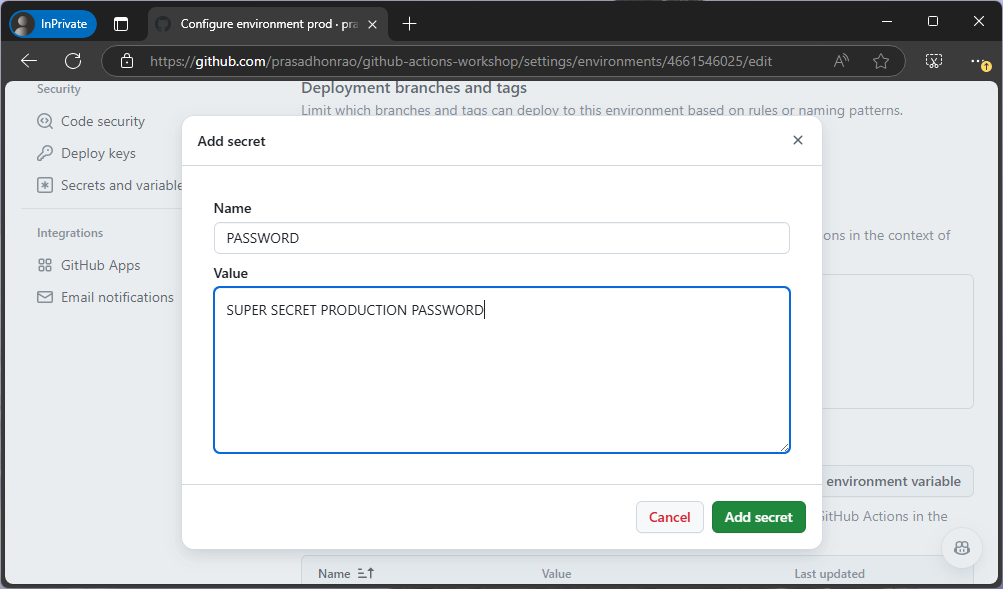
-
The environment secrets should now be added to their respective environments.
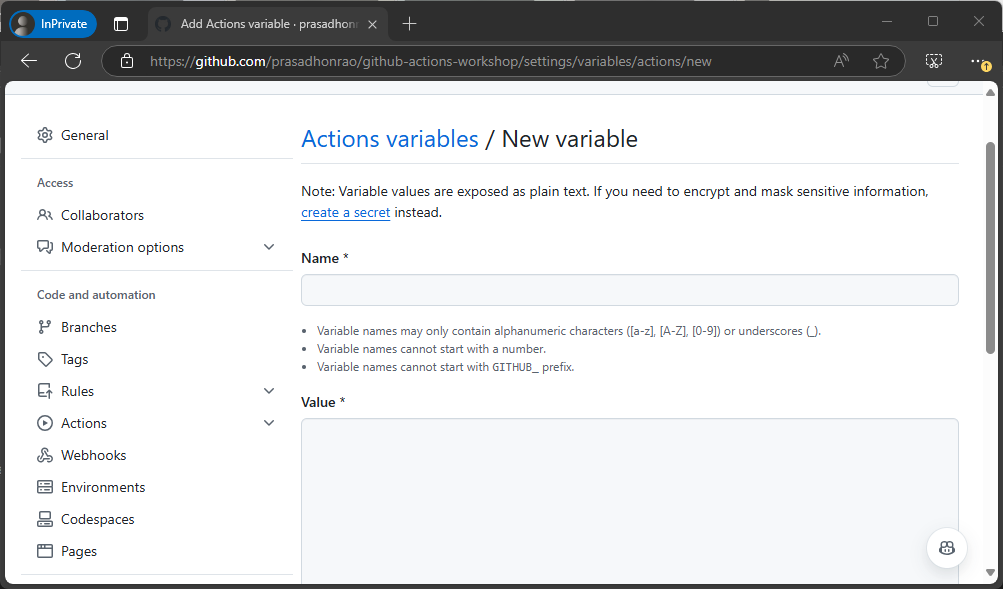
Step 4: Add Repository Variables
-
Go to your repository’s Settings tab and navigate to Secrets and variables on the left sidebar.
-
Click on the New repository variables button.
-
Enter the name as
REPOSITORY_VARIABLEand the value asrepository-variable. Click the Add variable button.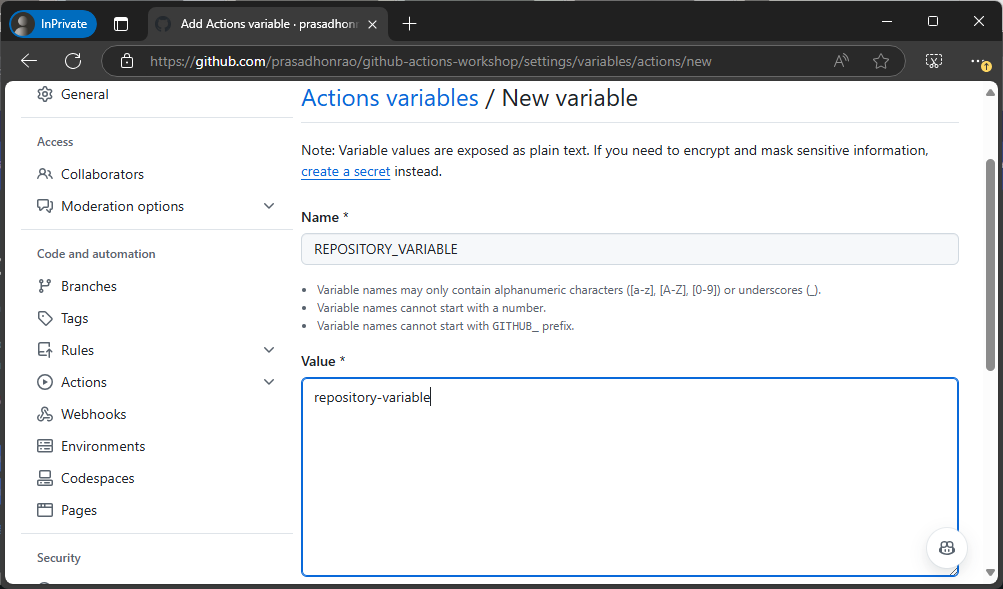
Step 5: Create a YAML Workflow Using the Starter File
-
Navigate to the Env Var and Secrets Starter File.
-
Copy the content of the starter file:
name: Env Var and Secrets -
In your repository, create a new workflow file under .github/workflows and name it env-var-secrets.yml.
-
Paste the copied content into the new file.
-
Commit the workflow file to the main branch.
Step 6: Use Environment Variables and Secrets in Workflows
-
Open the workflow file
[environments-and-secrets.yml](/.github/workflows/environments-variables-and-secrets.yml)in your repository. -
Since we have created multiple environments, we use a matrix strategy to run the workflow for each environment.
strategy: matrix: environment: [dev, prod] -
Set the context for the environment variables and secrets in the job by using:
environment: $ -
To access the environment variables in your workflow, use the following syntax:
- name: Display Environment Variable run: | echo "Building for environment: $" echo "ENVIRONMENT_NAME: $ENVIRONMENT" echo "ENVIRONMENT_NAME length: ${#ENVIRONMENT}" echo "ENVIRONMENT_NAME (partial): ${ENVIRONMENT:0:5}..." env: ENVIRONMENT: $ -
To access the environment secrets, use the following syntax:
- name: Display Environment Secret run: | echo "SECRET length: ${#SECRET}" env: SECRET: $ -
To access the repository variables, use this syntax:
- name: Display Repository Variable run: | echo "REPOSITORY_VARIABLE: $"
Step 7: Run the Workflow
-
Go to the Actions tab in your repository and click on the workflow Environments, Variables, and Secrets on the left sidebar.
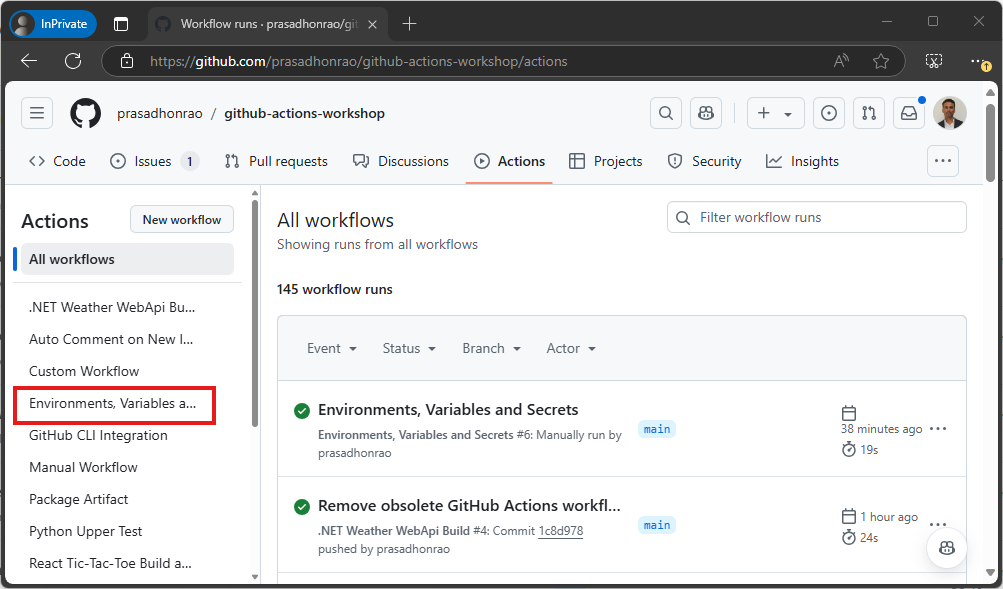
-
Let the workflow run for both the
devandprodenvironments.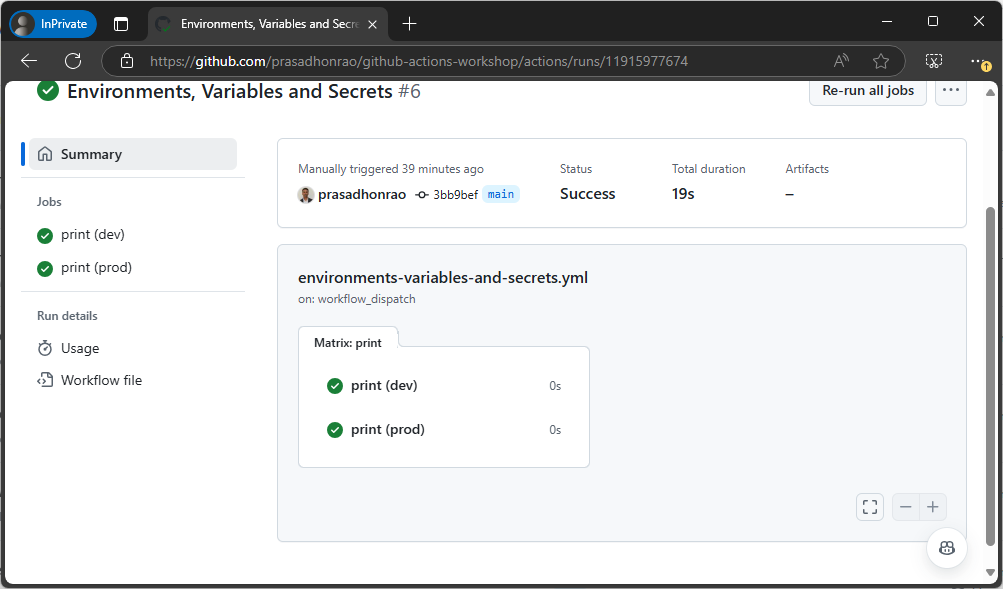
-
Click on the workflow run and check the logs for the environment variables, secrets, and repository variables.
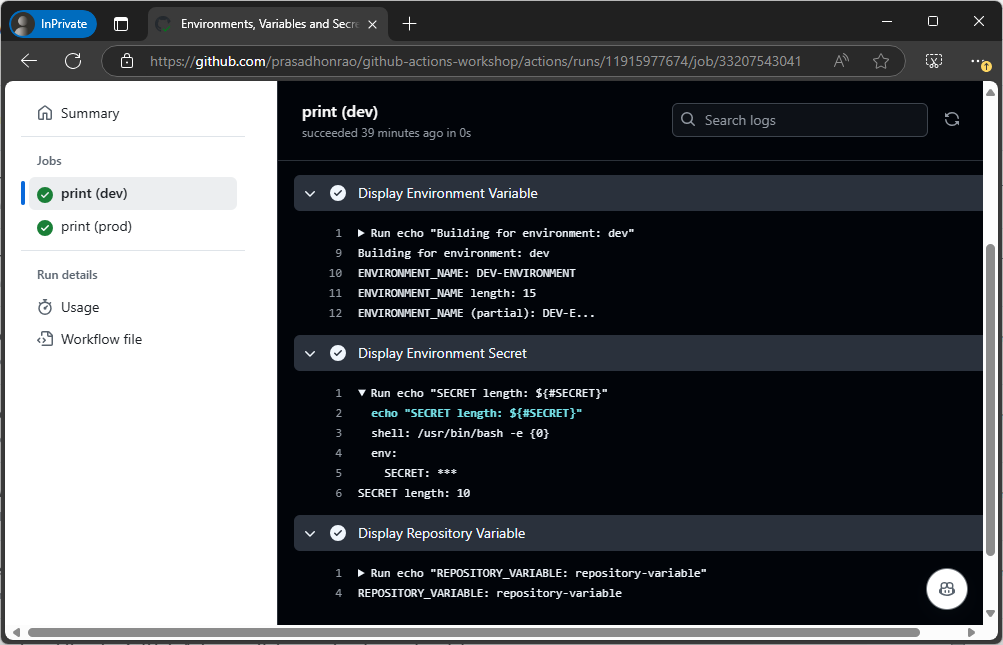
Summary
In this lab, you learned how to:
- Create environments in GitHub.
- Add environment variables and secrets to those environments.
- Use environment variables, secrets, and repository variables in your workflows.
- Run a workflow for multiple environments and check the logs for proper variable usage.